After the installation...
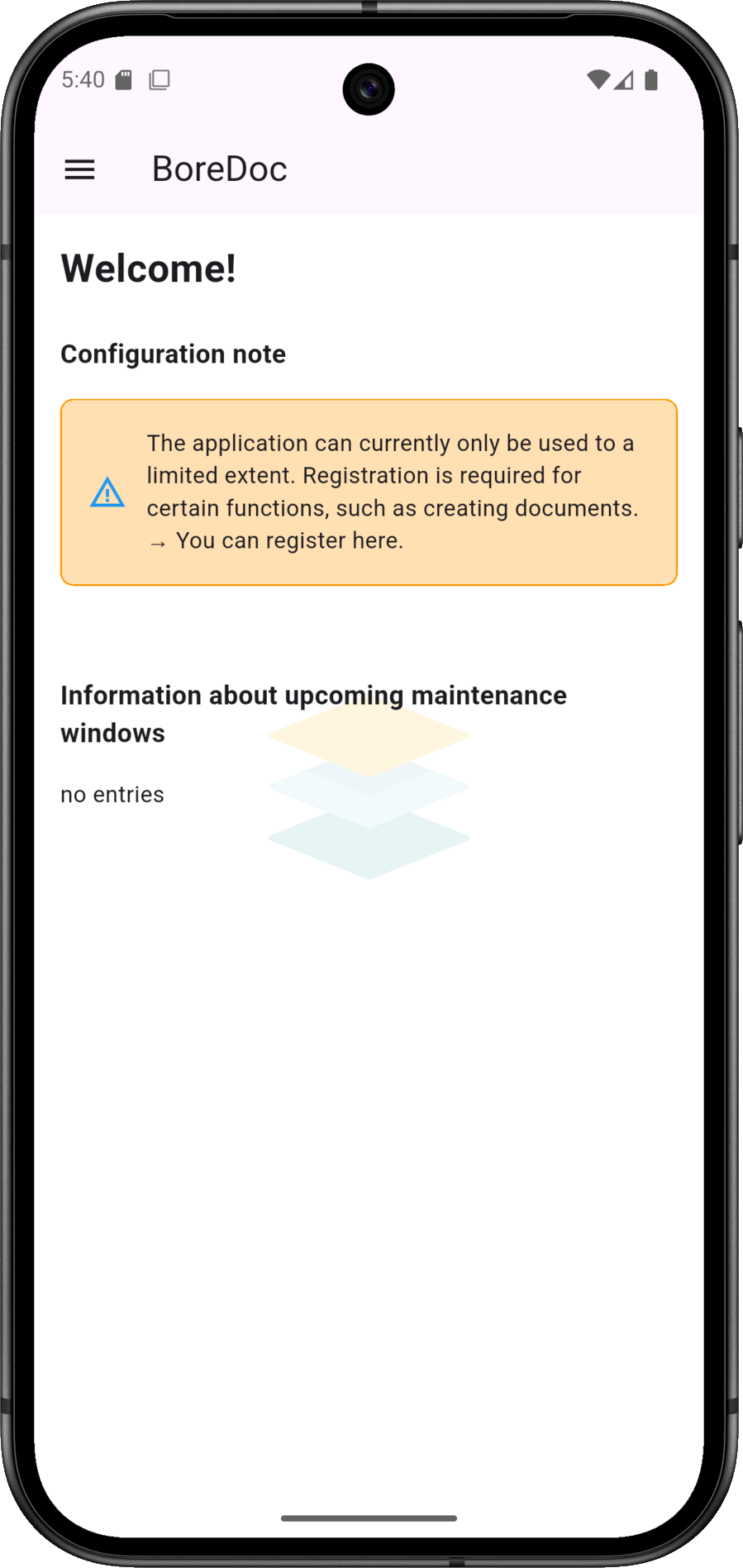
... The first step should be to register or transfer an existing registration. This is essential for creating documents.
With BoreDoc, you can record drilling data directly on site - structured, mobile and without paperwork. The app creates print-ready reports, also works offline and protects your data in accordance with the GDPR.
BoreDoc is currently available as an Android app for tablets and smartphones via the
Google Play Store
offered.
In addition, a
Brower version
for (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari), which is well suited for testing and short-term use. For long-term stable use - especially with regard to local data storage and controlled updates - the app version is recommended.
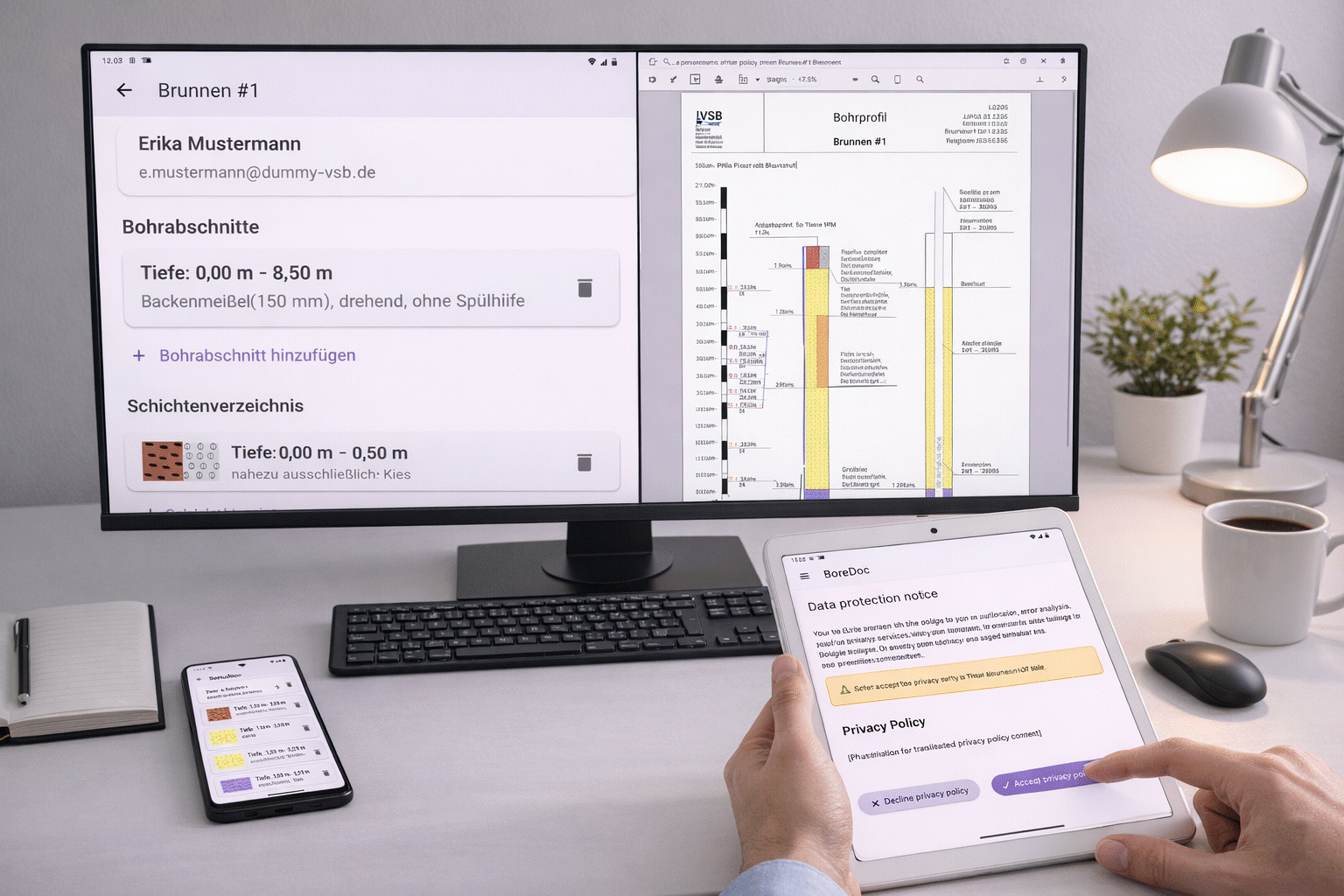
BoreDoc supports you in professionally documenting drillings and maintaining an overview at all times. From recording the strata to the complete drilling log, BoreDoc bundles all important information in one place. This turns complex data into clear structures that are convincing both in everyday life on the construction site and when working with clients, authorities or partners.
BoreDoc is a cross-platform app for structured drilling documentation. It replaces handwritten forms and reduces errors through guided, structured input. Different project types such as soil sampling, exploratory drilling or well construction are supported - including the simple creation of layer directories, drilling profiles and other documents.
In contrast to traditional applications, BoreDoc works flexibly as an app and web application. Multiple users can work with the current database at the same time - regardless of end device or operating system. Integrated multilingualism makes collaboration even easier: if an English-speaking user enters "Clay", a German-speaking user automatically sees "Ton". Language settings in the user interface and in the documents can be freely selected.
BoreDoc thus optimises teamwork - in a structured, efficient and even cross-language manner. Whether for engineering offices, construction companies or experts: BoreDoc makes drilling documentation efficient, transparent and reliable.

... The first step should be to register or transfer an existing registration. This is essential for creating documents.

Completed templates for contractors and technicians speed up the entry of repetitive information in the input process. If the templates are not filled in, a message is displayed on the start screen.
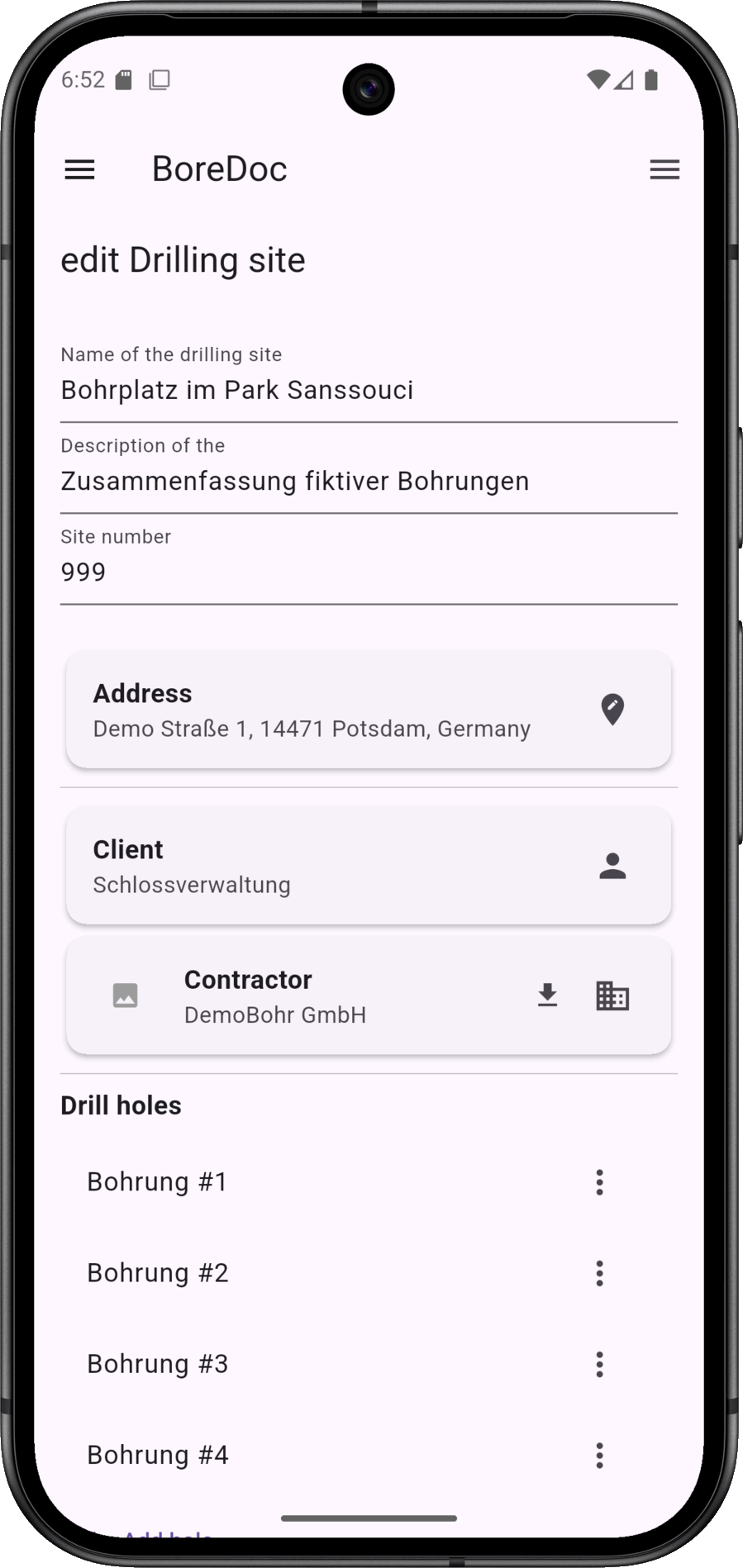
A drilling site includes master data, such as client and contractor, as well as several boreholes.
The context menu (sandwich icon top right) for the drilling site is also located here.
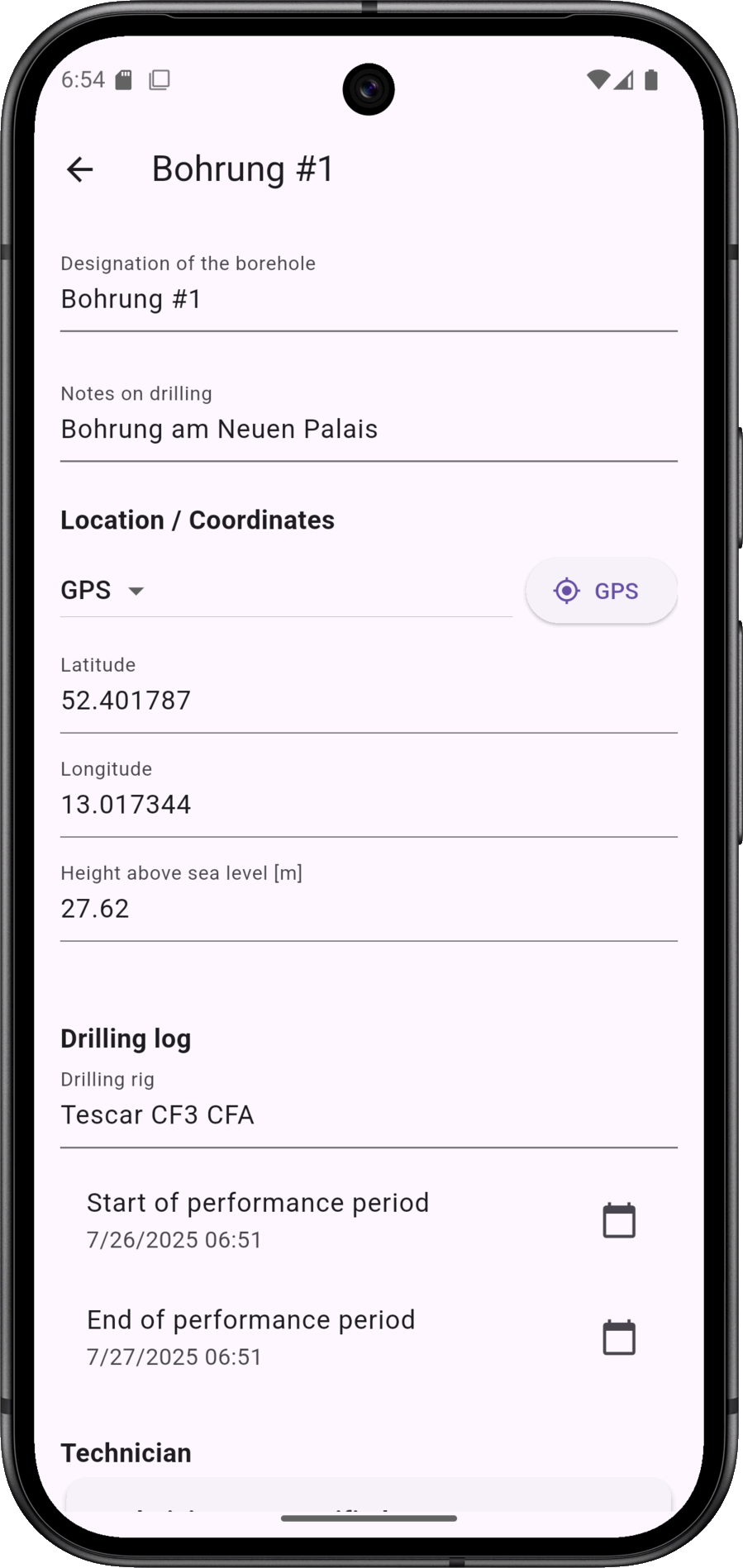
A borehole includes the usual data, such as name/designation, geo-coordinates, drilling log (execution period, technician, drilling sections, equipment used).
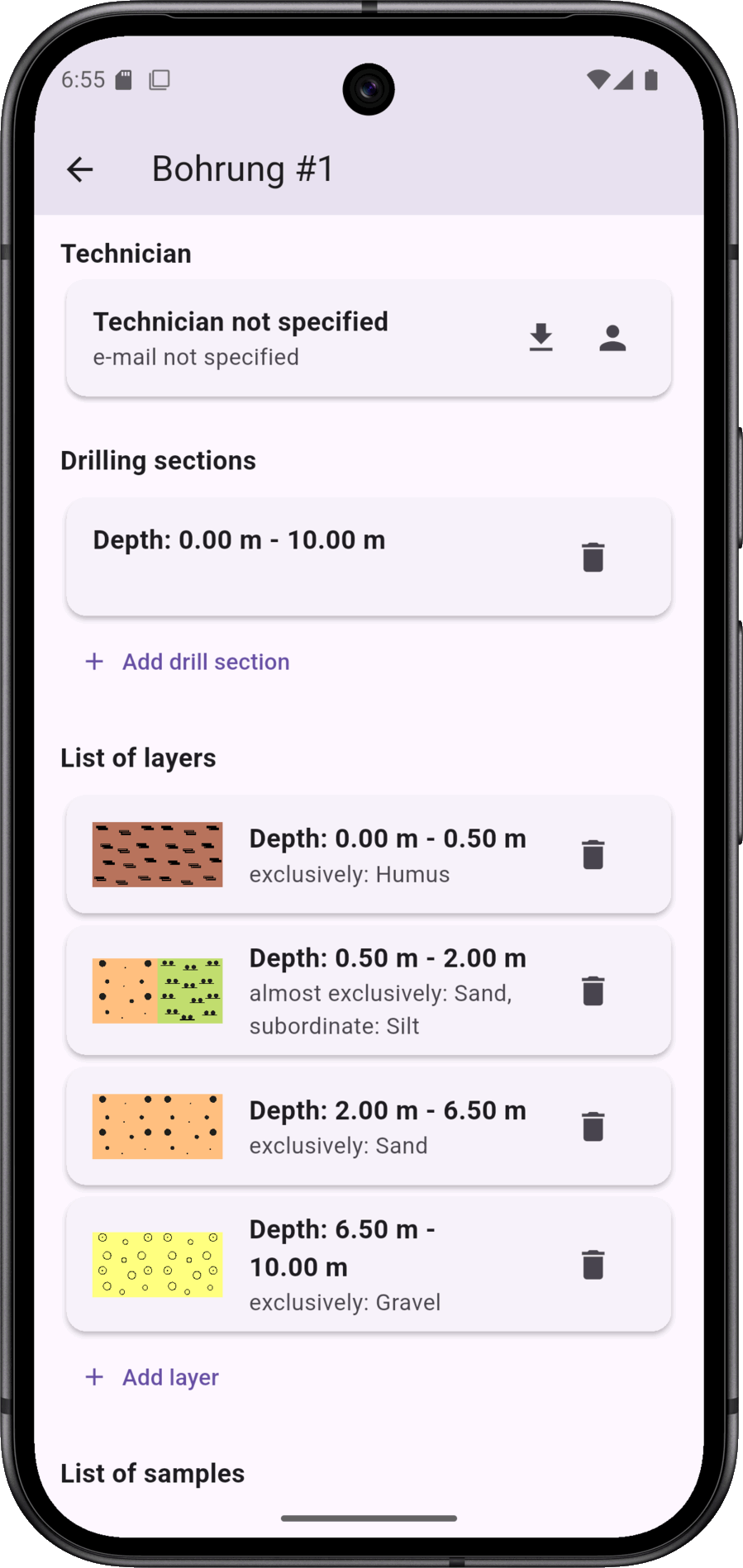
In addition, the borehole can be labelled with information on the soil layers, soil samples, water levels, backfilling and the development. Not all information is mandatory.
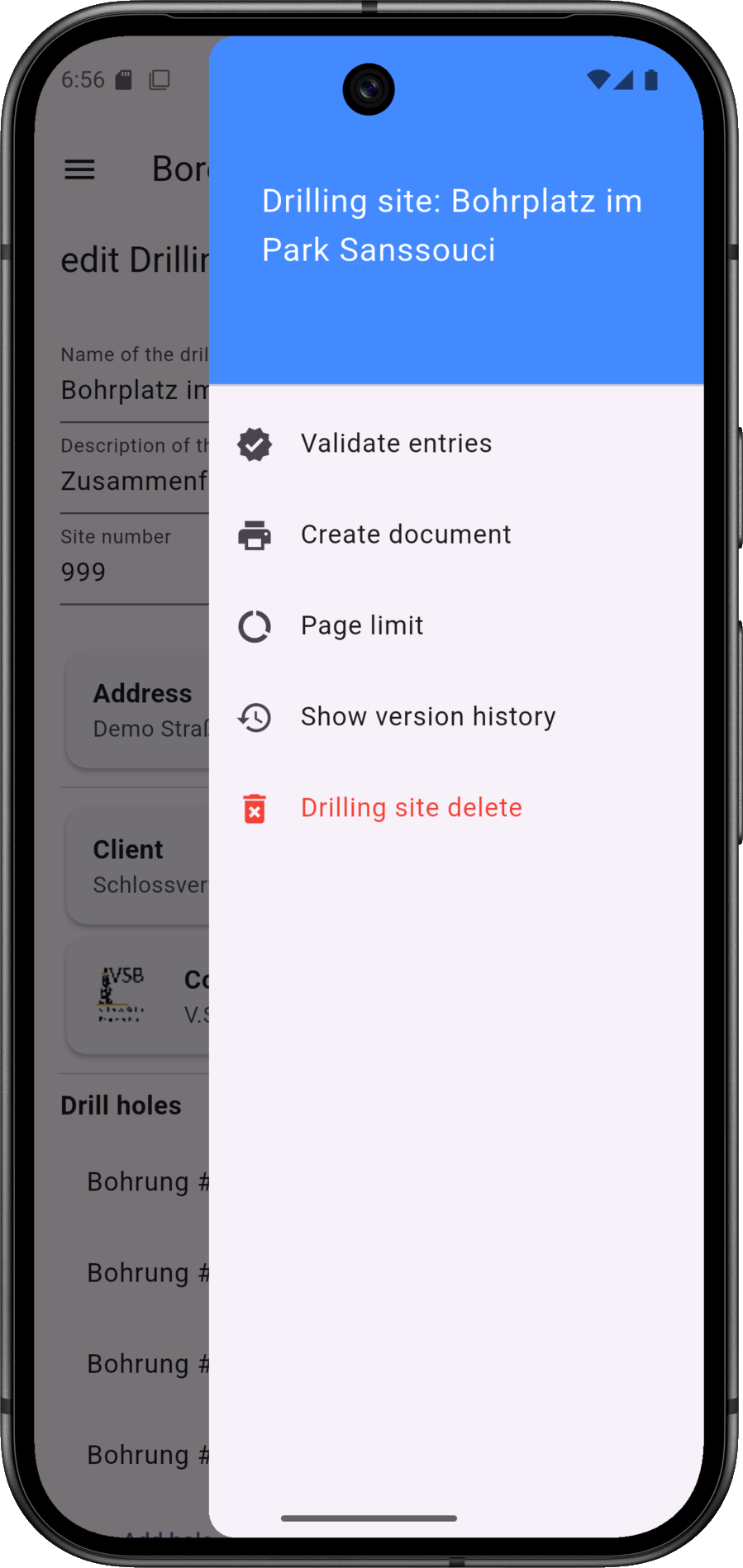
The context menu for the drilling site contains various functions, such as validating the entered data and triggering document generation.
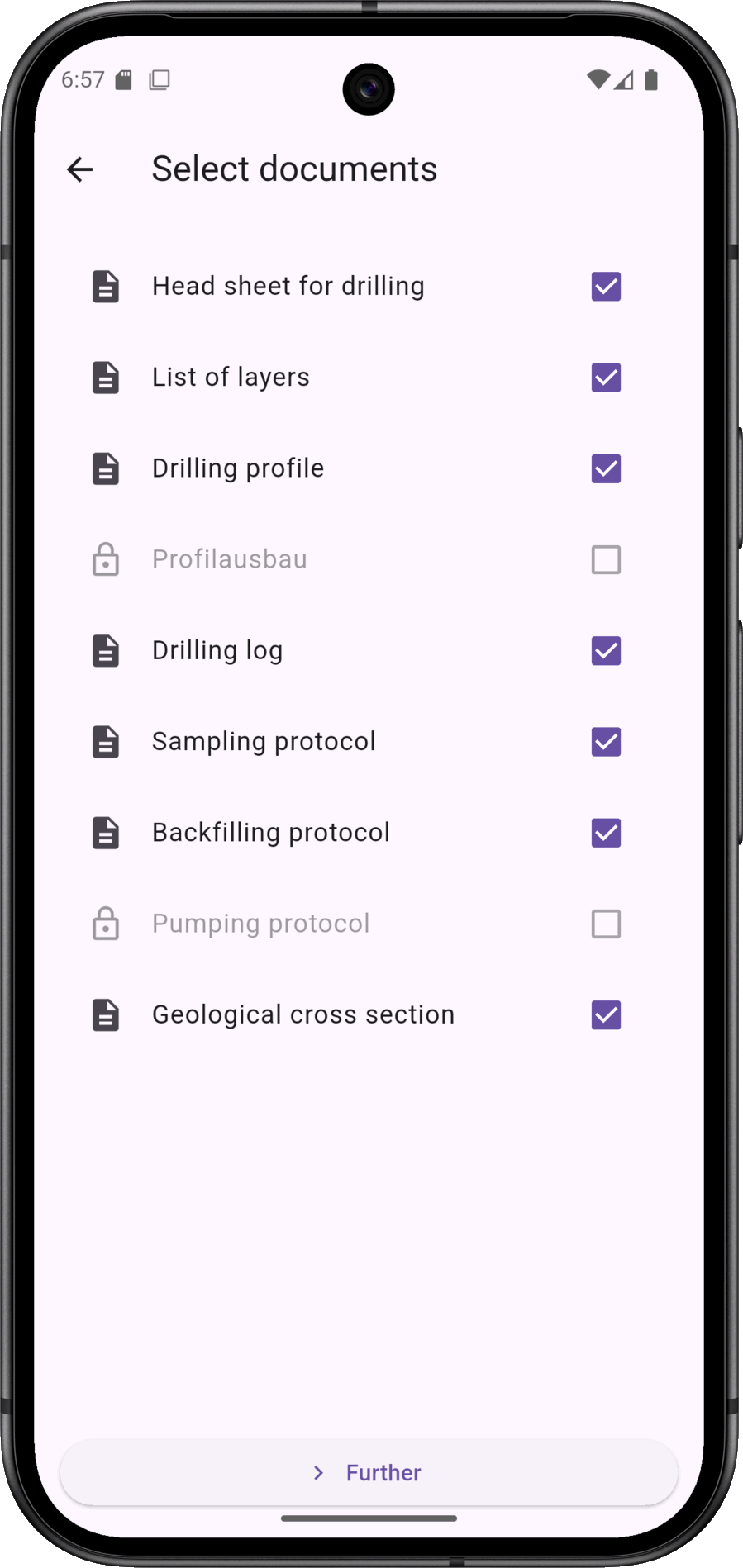
In the first step of validation, the documents to be generated are selected. These include the following: Stratigraphic log, drilling profile, drilling log, sampling log, geological section and others.
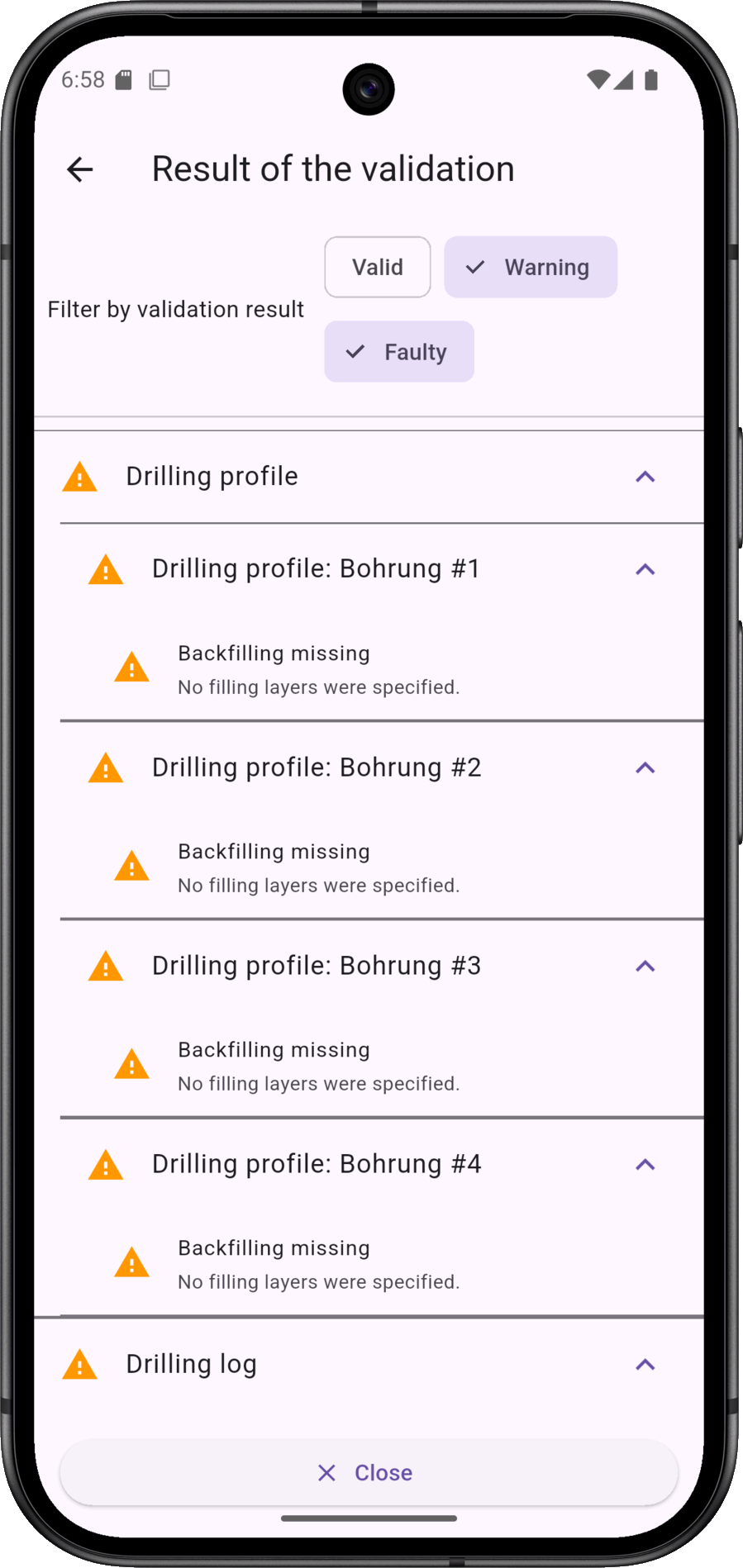
The validation result distinguishes between errors, warnings and valid. Warnings can be understood as hints. Example: Removal in the drilling profile is not possible if no information on backfilling has been provided.
This function is available online.
By requesting a document, the data from the drilling site is sent to the server, where the documents are generated. Depending on the connection speed, the process takes 5 to 20 seconds.
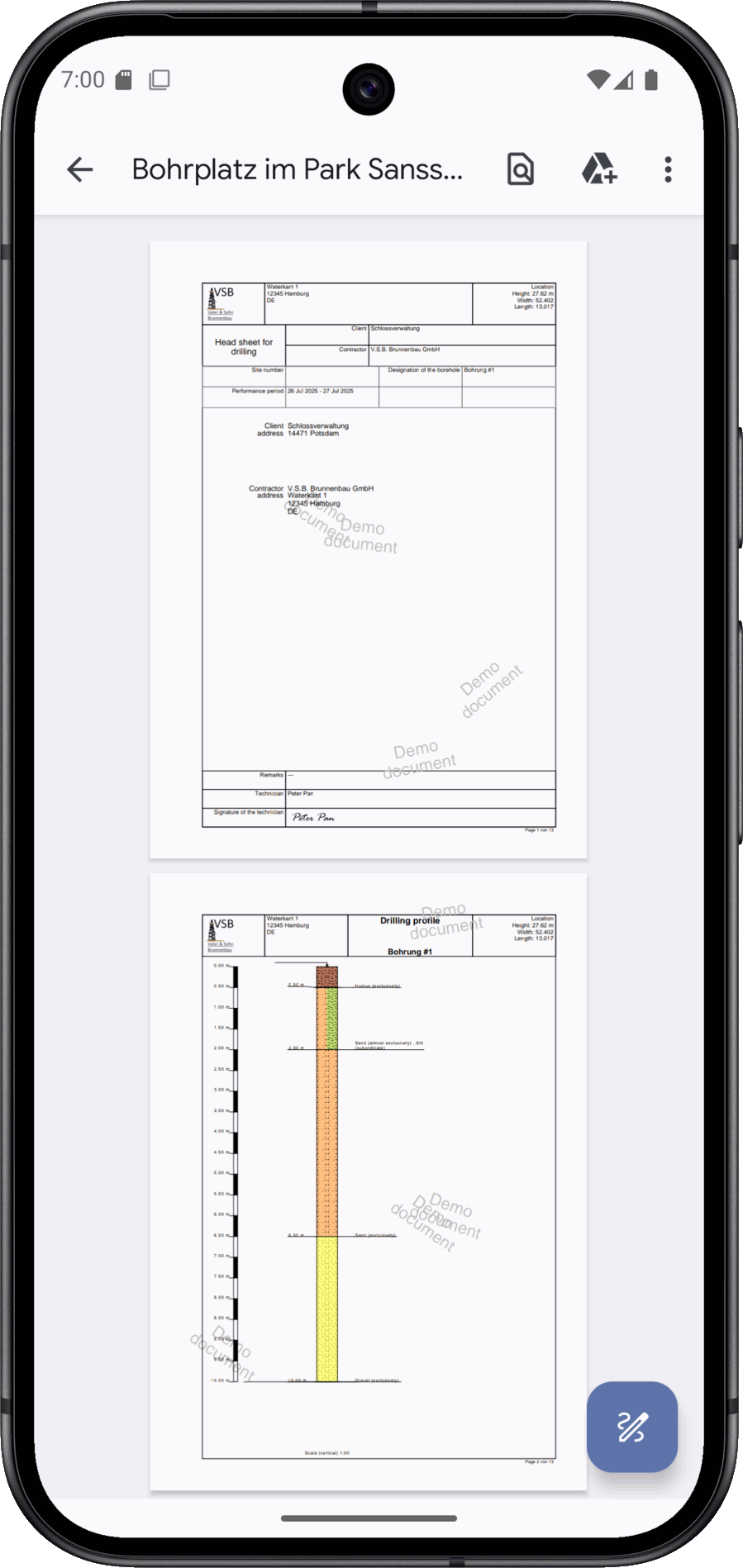
The documentation generated for the drilling site is transferred to your device as a PDF. You will need an appropriate display programme to view the document.
You can currently use BoreDoc completely free of charge. Our current focus is on further developing the functions together with our users and optimising them for practical use. A binding pricing model will be introduced at a later date. Until then, you can benefit from all the advantages without restrictions and without hidden costs.
A stratigraphic log is a key tool in geological and geotechnical exploration. It is used to document the soil and rock layers encountered during a borehole in a comprehensible manner and to present them in a fixed sequence. In this way, the subsurface is described in a structured form that is equally important for construction projects, environmental investigations or scientific questions. The overview creates a reliable basis for basing subsequent analyses and decisions on reliable data.
The properties of each individual layer are precisely recorded in the catalogue. This includes information on colour, grain size, consistency, moisture content and other characteristic features. Equally important are the depth details that mark the beginning and end of the layer. This creates a precise picture of the vertical structure, which remains comparable regardless of the drilling method. The organised structure makes it possible to depict even complex soil conditions in a comprehensible way.
A complete strata catalogue not only provides a snapshot of the drilling point, but also creates the basis for technical decisions. Engineers use it to select suitable construction methods, determine foundation depths or assess risks. At the same time, environmental experts benefit as information about possible pollutant layers or groundwater behaviour becomes visible. In research, it allows conclusions to be drawn about geological developments and the history of a region.
The care taken in the preparation has a direct impact on the usability of the bore log. Only if the information is consistent, detailed and comprehensible can it be used reliably by experts. The strata catalogue is therefore much more than just documentation - it forms the foundation for all further steps that are based on reliable knowledge of the subsoil.
DIN 4022 and DIN 4023, which contain specifications for the description and presentation of geological strata, are particularly relevant for stratigraphic logs. They ensure that geological findings remain comparable regardless of person and project. Internationally, ISO 14688, provides uniform standards for classifying and naming soils. These regulations ensure that strata catalogues are technically reliable, comprehensible and can be used across regions. This ensures comparability across national borders.
A borehole profile is the graphic realisation of the sequence of layers recorded during a borehole. It supplements the textual documentation with a clear visualisation that makes the subsurface visible in its vertical structure. This makes it possible to recognise at a glance which layers occur in which order, how thick they are and at what depth they lie. The aim is to make geological information clearly and directly accessible.
The representation is usually a vertical section in which each layer is clearly identified by symbols, hatching or colours. Depth information at the layer boundaries enables the exact location in the subsurface to be assigned. This creates a visual overview that allows quick orientation, independent of extensive texts. The drilling profile thus becomes an indispensable tool for geological documentation.
In practice, the drilling profile supports engineers, geologists and experts in evaluating the subsoil. It provides information on the load-bearing capacity, groundwater conditions or special risks and facilitates the selection of suitable construction methods. It is also an easy-to-understand basis for clients or authorities to make comprehensible decisions. It thus combines technical precision with a high degree of clarity.
The drilling profile also plays an important role in research. It allows conclusions to be drawn about the formation history of a region, documents geological processes and creates comparability between different locations. In environmental and hydrogeology in particular, it provides crucial information about the layer structure and possible water pathways. The drilling profile thus adds scientific value to its purely technical use.
The creation of drilling profiles is subject to established norms and standards to ensure uniformity and comparability. In particular, DIN 4023 (drilling profile), which regulates the graphical representation, and DIN 4022 (soil and rock characterisation) for the uniform description of layers. In addition, international standards such as ISO 14688 are used to name and classify soils. These standards ensure that drilling profiles can be understood in the same way regardless of location and time.
A drilling log is the comprehensive documentation of a borehole that records all key processes and observations during the drilling. It supplements the geological records such as the stratigraphic log or drilling profile with organisational, technical and time-related information. It thus provides a complete overview of the progress of a borehole and enables later traceability. The drilling log is therefore an indispensable working tool for construction projects, geotechnical investigations and scientific explorations.
The drilling log contains a description of the equipment and methods used, information on the start and end of drilling and the time schedule. Special incidents such as technical faults, drilling obstacles or unexpected geological findings are also recorded. This is supplemented by information on drilling depth, drilling progress and the aids used in each case, such as flushing fluids or pipework. The result is a complete and structured record that allows precise reconstruction of the borehole.
The practical importance of a drilling log lies primarily in its function as proof. It serves clients and authorities as proof of proper execution and enables experts to make a well-founded assessment of the results. The log can also be used to prepare technical decisions, assess subsoil risks and track cost developments. In the event of a dispute, it represents legally relevant documentation that safeguards the quality and progress of the drilling.
The drilling log also has its value in research and education. It documents not only the immediate results, but also the conditions under which a borehole was drilled. This information is indispensable for correctly classifying geological data and making it comparable. In this way, the drilling log makes a significant contribution to ensuring the transparency and traceability of geological investigations.
Established standards and guidelines exist for the creation and structuring of drilling logs. Particularly relevant are DIN 4021 (drilling, drilling equipment, drilling methods, drilling logs), which provide specifications for systematic documentation. In addition, regulations such as DIN 4022 (Soil and rock characterisation) are used to ensure a uniform description of geological findings. International standards such as ISO 22475 (Geotechnical exploration and investigation - Sampling methods and groundwater measurements) also contain specifications that can be used in connection with drilling logs.
If you have any questions or suggestions regarding data protection, you are welcome to contact us via the Contact form contact us.
We take the protection of your personal data very seriously. Personal data is any data that can be used to identify you personally. This privacy policy informs you about what data we collect, how we use it and what rights you have - both when using the boredoc.eu website and when using our BoreDoc app.
When you access our website, your device automatically transmits data for technical reasons. The following data is stored separately from other data that you may transmit to us:
We store this data for the following purposes:
Your IP address is only stored for a period of 90 days.
Legal basis: Art. 6 para. 1 lit. f GDPR (legitimate interest).
This website uses Google Analytics (Google Ireland Ltd., Dublin, Ireland).
Data collected: IP address (shortened), usage behaviour, device data
Purpose: Improvement of our offer
Legal basis: Art. 6 para. 1 lit. a GDPR (consent)
Data transfer: if applicable, third countries (e.g. USA) in accordance with EU standard contractual clauses
You can revoke your consent at any time or change it via our cookie banner.
Embedded videos from YouTube (Google Ireland Ltd.) can be displayed on our website. Your IP address is transmitted to Google when loading.
Purpose: Provide multimedia content
Legal basis: Art. 6 para. 1 lit. a GDPR (consent)
Our app uses Google Firebase. Services used:
The BoreDoc app works offline for the most part. Only certain functions such as synchronisation, QR code sharing and creating documents use a server connection.
We may use external providers within the EU for hosting and API operation.
You have the right to:
We reserve the right to amend this privacy policy in order to adapt it to changed legal situations or technical developments. The current version is available at Data protection retrievable.